| x | x |
 |
|
| x | |
|
IMMUNOLOGY
|
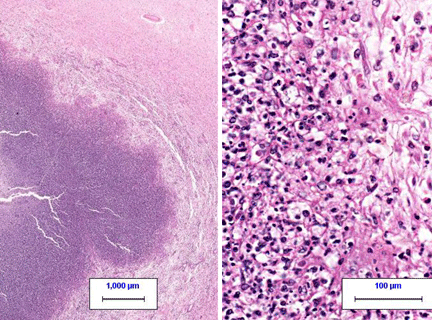
Pneumococcal pneumonia A 71-year-old man was hospitalized
for pneumococcal pneumonia. He responded well to antibiotics and was
sent home 6 days after admission. Two weeks later at a follow-up visit
he complained of continuing drowsiness and difficulty in using his left
hand. During the visit he suffered a grand mal seizure and was
hospitalized. There was a low grade fever and nuchal rigidity. His white
cell count was slightly elevated and his erythrocyte sedimentation rate
was elevated. There were no infiltrates in his lungs. Blood cultures
were done. Antibiotic therapy was begun and surgery was scheduled.
However, he developed papilledema and died soon thereafter. These images
are from the lesion in his brain. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Pathology questions by Dr Patsy Lill
|
