
|
|
|
IMMUNOLOGY
|
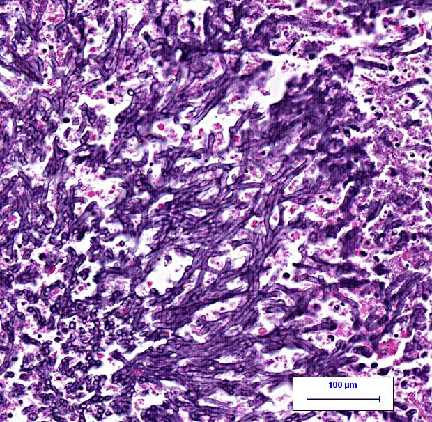
Dr Patsy Lill Kidney Transplant A 53-year-old kidney transplant patient presented with increasing BUN and creatinine. He was treated by increasing his immunosuppressive medications. Eighteen days later he developed a persistant cough, dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, hemoptysis and fever. He also had a heart murmur consistent with endocarditis. CT scan showed bilateral nodular infiltrates. Testing for TB, histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis was negative. Treatment with broad spectrum antibiotics did not improve his condition. Immune testing showed defective neutrophil function as well as suppression of lymphocyte and macrophage function. Sputum samples obtained by bronchoscopy showed the organism shown below. He was placed on Voriconazole but succumbed to the infection 2 weeks later. Autopsy disclosed the organisms shown below in his lungs and colonizing his mitral valve.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Pathology questions by Dr Patsy Lill
|
